Web Frameworks
CSC 342 - Web Technologies
Software Frameworks
A framework provides generic functionality that can be selectively changed by additional user-written code
Characteristics of frameworks:
Inversion of control: the control flow of the program is dictated by the framework, not the caller
Extensibility: the user can add code to provide specific functionality
Non-modifiable framework code: the framework code is not intended to be modified but accepts user-implemented extensions
Web Frameworks
A web framework is a software framework designed to support the development of web applications including web services, web resources, and web APIs
Types of web framework architectures:
Model-view-controller (MVC)
Three-tier organization
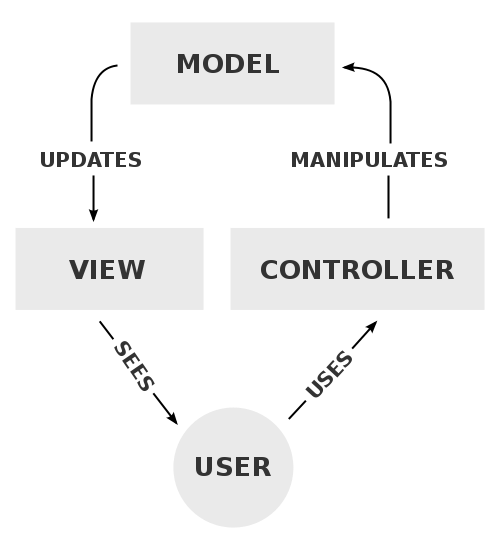
Model-View-Controller (MVC)
The MVC architecture divides a given application into three interconnected parts in order to separate concerns:
Model: manages the data, logic, and rules of the application
View: is an output representation of the information
Controller: accepts input and converts it to commands for the model or view
Types of MVC architectures:
Push-based: use actions that do processing and then “push” the data to the view layer
Pull-based: the view layer can “pull” data from multiple controllers as needed
Model-View-Controller (MVC)
Three-tier architecture
The three-tier architecture is a client-server software pattern divides the application into independent layers:
Presentation tier: displays information to the user
Application tier: controls the application’s functionality
Data tier: provides data persistence mechanisms and a data access layer with an API for the application tier
Features of Web Frameworks
Web template system
Caching
Security
Database access, mapping and configuration
Scaffolding
URL Mapping
Ajax
Web services
Web resources
Web Template System
A web template system uses a template processor to combine web templates to form finished web pages
A web template system is composed of the following components:
Template engine: the processing component
Content resource: the input streams
Template resource: the template specified according to a template language
Web template systems are used to separate the business logic from the presentation logic
Kinds of Web Template Systems
Template systems are classified based on when the assembly happens:
Server-side: run-time substitution happens on the web server
Client-side: run-time substitution happens in the web browser
Edge-side: run-time substitution happens on a proxy between the web server and browser
Outside server: static web pages are produced offline and uploaded to the server
Distributed: run-time substitution happens on multiple servers
Web Cache
A web cache is a technology used for temporarily storing web documents to reduce bandwith usage and server load
HTTP provides three mechanisms for controlling caches:
Freshness: allows a response to be used without re-checking on the origin server
Validation: can be used to check whether a cached response is still good after ir becomes stale
Invalidation: cached reponses can be invalidated as a side effect of another request, such as a POST, PUT, or DELETE request
Security
- Some web frameworks provide functionality for authentication and authorization that enable the web server to identify users of the application and restrict access to functionality based on some defined criteria
Data Access, Mapping and Configuration
Many web frameworks provide a unified API to a database backend enabling a web application to work with a variety of databases
Web frameworks in object oriented languages typically provide an object-relational mapping (ORM) the maps objects to tuples
Scaffolding
Scaffolding is a technique used in some MVC frameworks in which the programmer can specify how the application database may be used
The specification, along with pre-defined code templates, is used to generate the code that the application can use to perform CRUD operations
URL Mapping
The URL Mapping or routing facility is the mechanism by which the framework interprets URLs
In MVC frameworks the URL mapping system routes a URL to the appropriate controller
URL mapping systems can interpret URLs in different ways:
Pattern matching: match the provided URL against predetermined patterns using regular expressions
Rewriting techniques: translate the URL into a form that the underlying engine will recognize
Graph traversal: decompose the URL in steps that traverse an object graph of models and views